Drinking alcohol has heavy repercussions on a person’s health, family life, and social life. But until now, experts and physicians used to state that drinking alcohol in moderation is okay.
But a new study has revealed that even drinking in moderation hurts the brain. It makes the brain age faster and causes premature cognitive decline.
Alcohol and its ill-effects
Alcohol affects almost all parts of the body. This is done directly as well as indirectly. The deleterious effects are on the liver predominantly. Liver cirrhosis and liver failure occur in chronic alcohol drinkers.
And this is the end stage and causes a fatality. It can affect the stomach and cause gastritis. It also leads to other organ damage including the brain.
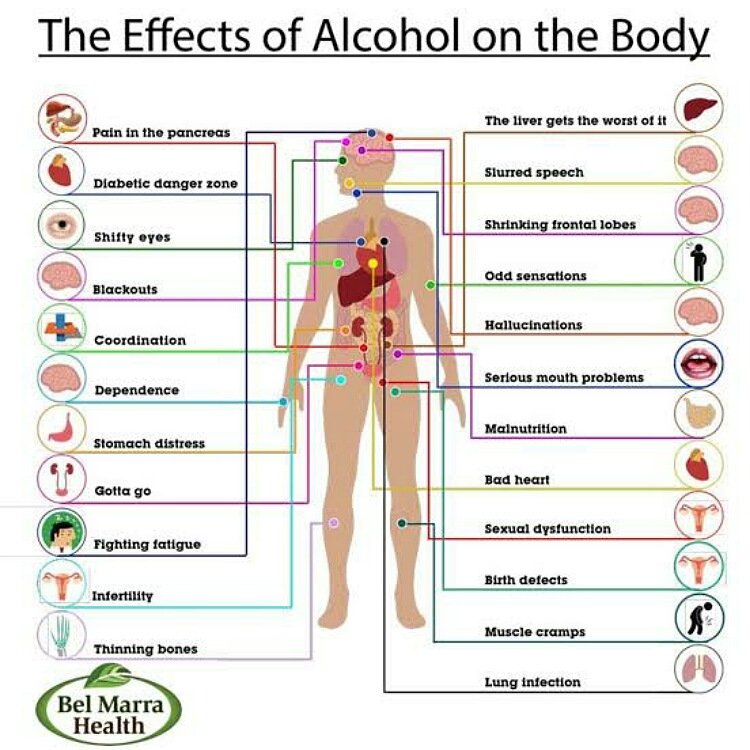
But until now, experts used to state that alcohol consumption in moderate amounts does not cause damage. But a new study has negated this thinking. These recent findings reveal that even alcohol in moderation leads to rapid deterioration of the brain. It ages faster compared to those who do not drink. This forces us to rethink social drinking. How much alcohol in a week is healthy?
Details of the new study
This study is published in the July 2022 issue of PLOS Medicine. 20965 participants formed the sample group. Their mean age was 55 years. 2.7% of these recruits drank no alcohol.
Whereas the remaining participants consumed a mean of 18 units (six glasses of wine or 7.5 cans of beer) of alcohol per week. One of the authors Anya Topiwala from the University of Oxford said:
“In the largest study to date, we found drinking greater than 7 units of alcohol weekly associated with iron accumulation in the brain,”

Anya added:
“Higher brain iron in turn linked to poorer cognitive performance. Iron accumulation could underlie alcohol-related cognitive decline.”
Expert opinion on the study
These new findings imply that even moderate alcohol drinking leads to cognitive deterioration. Emma Laing from the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics states:
“The researchers found that moderate alcohol consumption was associated with greater iron accumulation in the basal ganglia, a group of brain regions that helps us perform cognitive, emotional, and movement-related functions,”
“Higher levels of iron in the basal ganglia were associated with poorer measures of cognitive function.”

Explaining further, Emma said:
“The brain is very sensitive to changes in iron metabolism,”
“Abnormally high iron in the brain has been associated with oxidative stress, which leads to neuronal damage and cell death.”
To prevent this early brain aging, one should ideally totally avoid alcohol. If still one wants to consume, prefer light-alcohol, non-alcoholic, or alcohol-free beverages.
One can reduce alcohol intake by consuming 1 or 2 glasses of plain water with each glass of alcohol. This will curtail overconsumption. Additionally, avoid having alcohol on an empty stomach.
Read more: Alcohol hangovers: are home and commercial remedies effective?
But if cutting down or abstinence is difficult, involve counselors and recovery programs. They can help you cope with the problems of alcohol addiction and help overcome them.
