Probiotics are useful for gut health. Studies have shown that it has a lot of other health benefits too. This includes protection of heart, lowering of blood cholesterol and blood sugar, and reduction of chronic inflammatory diseases. The journal Frontiers in Nutrition has published a new study about Brevibacillus laterosporus BL1 that could help in fighting obesity. This bacilli from earthworm intestine helped mice on high fat diet to have lesser weight compared to control mice.
The background of Brevibacillus laterosporus BL1
The Chinese researchers involved in the study stated that it is confirmed that the widely available probiotic species of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria are useful in lipid metabolic disorders such as nonalcoholic fatty liver and obesity. They control intestinal barrier function, energy metabolism and inflammatory response of the body.

The Chinese agricultural and animal nutrition scientists said:
“Despite these positive outcomes, a recent systematic study showed that the species of probiotics that are effective in the prevention or treatment of adiposis are scarce, and limited probiotics produce a discrete benefit in clinical applications.”
They continued:
“For this reason, there is an urgent demand to identify novel strains with anti-obesity properties and the functional mechanisms involved in their actions.”
Studies have shown that Brevibacillus laterosporus BL1 synthesizes various antimicrobial substances such as polyketides, chitinase, non-ribosomal peptides, and antibiotics. A study of this probiotic in porcine model showed that it has the potential to mobilize fat and aid in obesity management. But at that time, the mechanism of action was unclear. The researchers hypothesized that it improves gut microbiome dysbiosis and thus decreases excessive fat formation.
The study details and findings
40 five-week old C57BL/6 male mice were randomly put in one of the 4 groups: control diet, high fat diet, high far diet with Brevibacillus laterosporus BL1 and high fat diet with supernatant of B. laterosporus BL1 for 8 weeks. The scientists monitored the weight, fat deposition, serum lipids, intestinal flora composition, chronic inflammation, insulin resistance, and colonic short chain fatty acids or SCFAs.
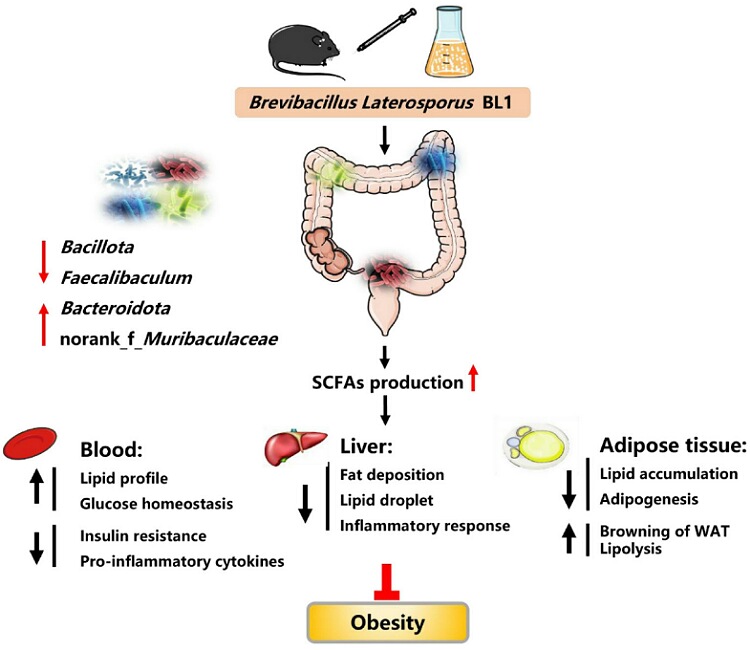
The findings showed that the B. laterosporus BL1 helped reduce fat deposition by 41.26% compared to that in high fat fed mice. The lipid profile, chronic inflammation, and insulin resistance were also better in the treated group of mice. Their gut flora dysbiosis improved and bacteria producing SCFAs increased in the treated mice. But in the supernatant treated group, no significant benefit in gut flora was found.
Conclusion
The study has shown that the earthworm intestinal bacteria does have the potential to improve gut flora in mice. This in turn leads to improvement in weight management and lipid profile of blood. Moreover, it reduces chronic body inflammation and also increases insulin sensitivity. This helps in reversing and prevention of chronic diseases and inflammation.
Also, read Greek yoghurt: its role in reducing visceral fat
Thus, one can synthesize probiotics from the earthworm intestines and use it commercially and medically for the benefit of humans. It could enhance their health and overcome chronic issues that come with age.
