Psoriasis is an immune condition of the body in which epidermal cells of the skin proliferate faster than usual. There are topical and oral medicines to control this condition but there is no cure of it. Diet might also play a role as a complementary therapy. Mostly, an anti-inflammatory diet can assist in suppressing the fast growth of the skin cells and providing some relief from the symptoms.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a condition of the body in which immune response is involved. It is a psychosomatic disease in which the epidermal cells of the skin grow faster than the normal rate of 21 to 28 days. In just a few days, the skin replacement occurs and this leads to formation of plaques on the surfaces. These patches on abnormal skin areas are rough, dry and scaly and leave weeping surfaces and bleeding points when the upper layer is removed.
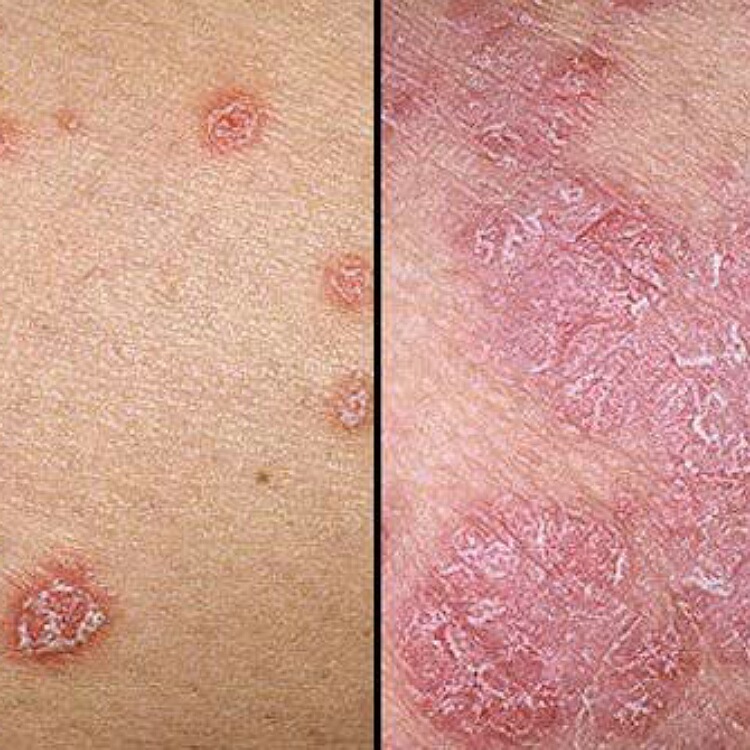
In the UK, around 1.8 million people are affected with this condition. This disease shows two peaks. It starts at around young adulthood or after the age of 50. The patient also has joint and soft tissue involvement. There may be arthritis and predominantly the small joints of hands and feet are involved. Moreover, recent studies have shown that in this condition, T cells of the body are hyperactive. The areas of the body most affected are scalp, hands, feet and also genitalia. Certain medicines both topical and systemic can control the condition but it lacks a cure.
Foods and their role in treatment of this condition
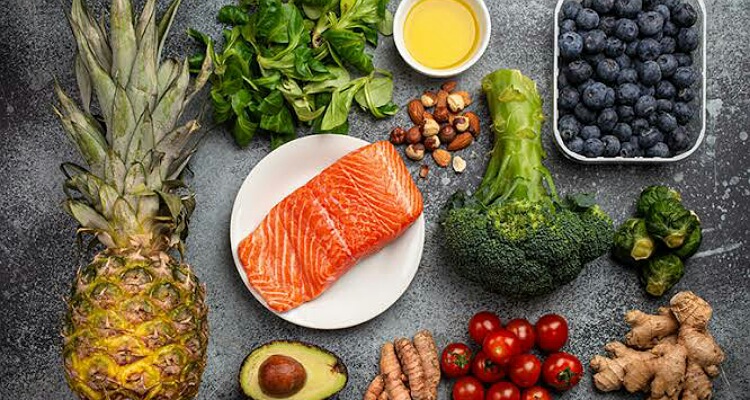
Diet and certain foods can help in alleviating the itchy and painful symptoms. These include anti-inflammatory foods. Nutritionist Rebekah Lamb states:
“Because psoriasis is an inflammatory condition, eating anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce its severity,”
“Most fruit and vegetables, as well as herbs rich in antioxidants, are all anti-inflammatory.”
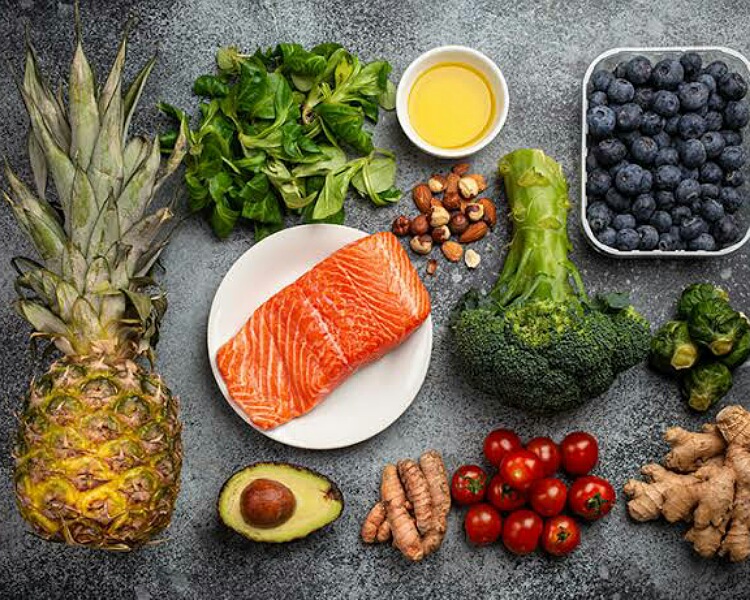

Besides fruits and vegetables, Rebekah recommends patients to have lots of nuts, seeds and seafoods such as salmon. She advises:
“Healthy fats – such as those found in salmon, nuts and seeds – also help to reduce inflammation in our bodies and skin”
“Fish oil supplements can be beneficial if you’re not a fan of eating seafood.”
Cold winter months can cause a flare up of the condition. Therefore, such time of the year requires special care and proper diet.
What does the Psoriasis Association say?
The Psoriasis Association of the UK opine that no direct link between food and psoriasis has been established. It says:
“There has been some research in other inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, that suggests that eating foods that reduce inflammation in the body may be helpful,”
“There is no definite evidence to say that this works in psoriasis but, again, it may be an approach that some people find helps.”
Also, read here:The best and worst foods for psoriatic arthritis!

The charity added that gluten free diet might help. One can keep a food dairy to know which foods trigger the symptoms to increase.
