The aim of athletes and fitness people is to enhance physical performance. They consume a number of supplements for it including proteins and branched chain amino acids. Research has revealed that dietary nitrates too help in this. A new study has backed this earlier finding.
Dietary nitrates and muscle performance
Exercises are to make muscles stronger and increase the muscle or physical performance. A normal adult does not require so much of a great physical performance and output. But this is not the case with athletes and those who regularly attend gyms. They have to up their body performance. And for this they rely on nutrition from diet as well as supplements.

These supplements have extra protein, branched chain amino acids (muscle foods), electrolytes, and vitamins that assist in energy production. Taken pre and post workout, these supplements boost the muscle strength and increase their performance. Also, they assist in recovery of these muscles.
Studies have shown that dietary nitrates can enter the blood stream and get converted to nitric oxide. And this increases work performance and output.It has a positive impact on cardiovascular system too. These nitrates are rich in beet root, its juice, dark green leafy vegetables such as spinach and in arugula.
Mechanism of action of nitrates
Previous studies have shown that dietary nitrates have a positive influence on the muscle strength and cardiovascular function. Scientists believed that these nitrates exert their action by converting to nitric oxide in the body. This nitric oxide is a vasodilator. It acts on the blood vessels, dilates them and improves the blood flow to the muscles and heart.
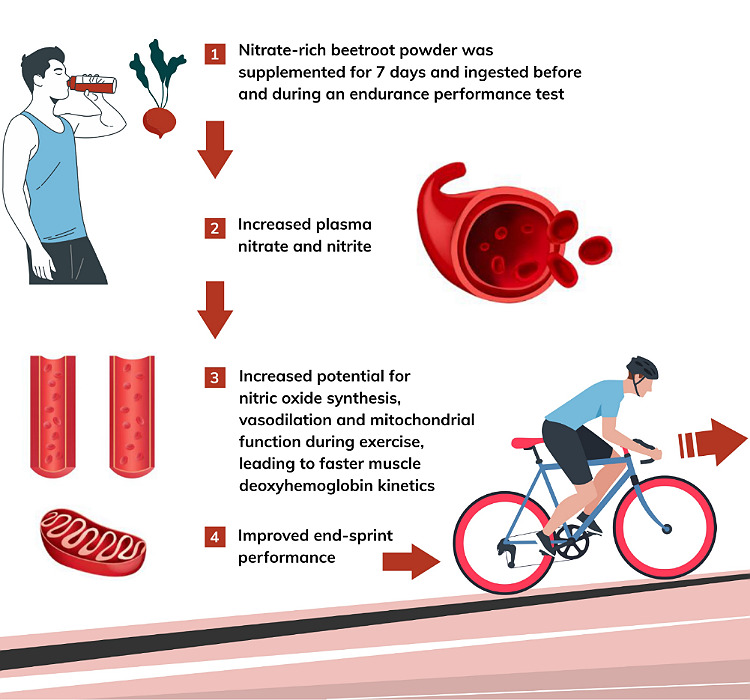
And now a new study from the University of Exeter has revealed that the nitrates also directly act at the muscular level and improve force of these muscles. The study was jointly carried out by the researchers from the University of Exeter in the UK and the US National Institutes of Health. And the study article is published in this month’s issue of the journal journal Acta Physiologica.
The study
Researchers took 10 recruits for the study. They were either given potassium nitrate supplements or a placebo. After an hour of consumption, each of them did 60 contractions of the quadriceps or thigh muscles. A special machine was used for this purpose.
Those on potassium nitrate had 7% more muscle force in the quads compared to those who had a placebo. Co-author, Andy Jones said:
“Previous studies have shown that, when plasma nitrate and nitric oxide levels are increased following nitrate intake, exercise performance is improved — and the same thing was true in this study,”

Andy further elaborated:
“A novel finding was that it was the muscle (rather than blood) nitrate levels that were most closely related to the improved muscle force production,”
Also, read Skipping Breakfast: unhealthy and harmful for the body muscle mass
This was confirmed by means of muscle biopsies after the exercise session and at three hours. Nitrates probably act on the muscle and reduce its oxygen demand. It also increases intracellular calcium (a trigger of muscle contraction). This muscle contractility improves and with same amount of oxygen, force is more.
