Microscopic colitis is an inflammation of the large intestine leading to frequent, watery and loose motions. Medicines help in overcoming this problem but diet and lifestyle are equally important in providing relief to the patient. What type of diet helps in easing the condition?
What is Microscopic colitis?
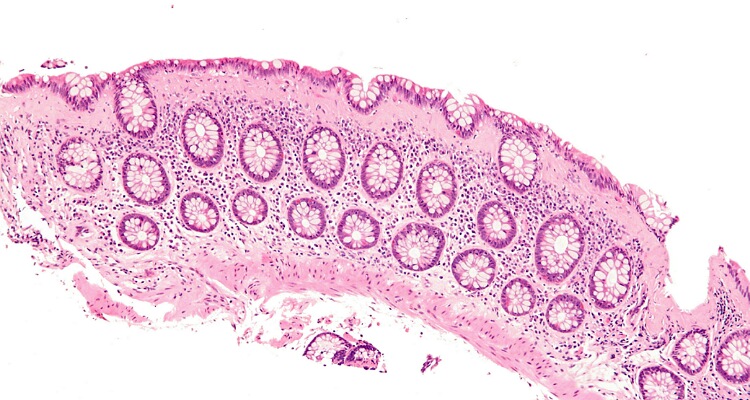
Microscopic colitis is a clinical entity in which there is inflammation of the large intestine. Flexible sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy cannot diagnose this condition. Only a biopsy of the local tissue clinches the diagnosis.
The symptoms include watery recurrent diarrhoea. It is chronic and non bloody. The patient also experiences abdominal cramps and discomfort. There is unintentional weight loss with fatigue and dehydration. Muscle and joint pains also are present in some individuals.
The cause is not clear. In some, there is spontaneous resolution. Whereas, other patients require medications to control the condition. Diet and lifestyle play a role in therapy and prevention of the condition. What type of diet is beneficial in this disorder?
Role of diet
Research is ongoing in this field in order to study the relationship between diet and microscopic colitis (MC). Until now, researchers have failed to link the condition with diet. No particular food consumption causes the inflammatory disease.
In 2016, Swedish scientists published a paper on MC. In their study, they followed up 135 patients of microscopic colitis over 22 years. And they monitored the every study individual’s daily intake of sucrose, carbs, protein, saturated fats, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, fiber, omega 3 fatty acids, omega 6 fatty acids, and zinc.

They analyzed the findings and tried to find a correlation between these food components and MC. But they failed to find any association between these food elements and MC.
However, certain foods can definitely help in easing the condition. There is not much research in this direction but probiotics is believed to have a beneficial role in it. Probiotics do help in other gut conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome and ulcerative colitis. Extrapolating those data, it might seem that they might also help in MC. But research in this area is lacking.
Nonetheless, the patient of MC should have lots of water. This is to replenish the water loss in stools and to prevent and treat dehydration.
Foods that can worsen MC
Certain foods can exacerbate this gut condition. These foods include caffeine, lactose and high fats foods. A medical doctor can review the patient and analyze the stools to know what diet would be suitable for a particular case. If the stool analysis shows that there are liye of fat globules in it, then the patient should avoid high fats foods.
People can keep a food diary and track which foods help or worsen the symptoms. One can even try elimination diet and reintroduction with symptom observation. High fiber diets may also harm the gut in these cases. Some people may have simultaneous gluten intolerance. Hence gluten foods are to be avoided in them.
Also, read Diarrhoea: Foods to eat and those not to eat!
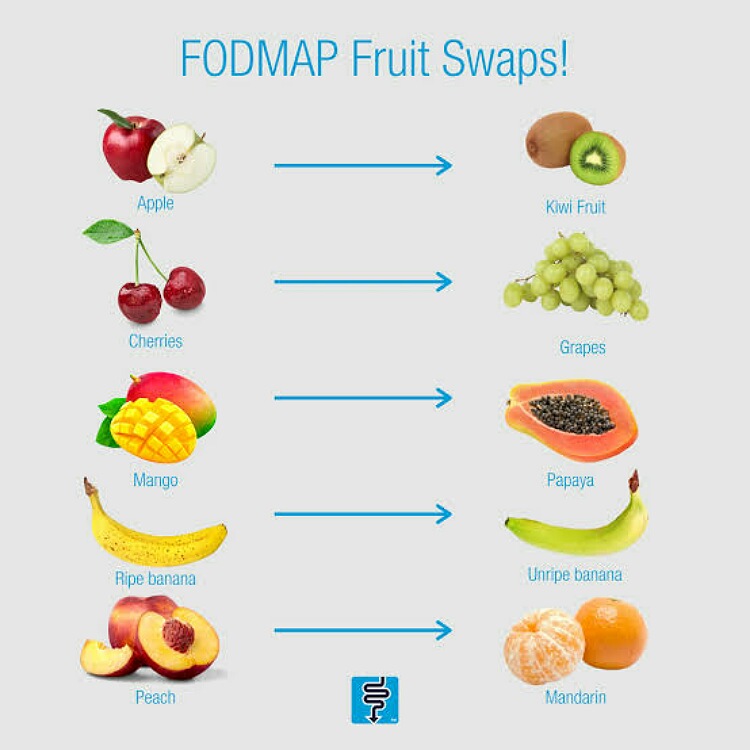
Similarly, FODMAPs or fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols can cause worsening of symptoms.