MSG or monosodium glutamate or sodium glutamate is a chemical. It is found in some foods naturally. But manufacturers and chefs add it to foods to enhance their flavor. Is it good and healthy? Can one have it daily?
Monosodium glutamate or MSG
Monosodium glutamate or MSG is the sodium salt of glutamic acid. It is a chemical with the chemical formula of C5H8NO4Na. It is a white, odorless, crystalline powder found naturally in foods such as tomatoes and cheese. It is used in a number of Chinese foods.
It was in 1908 that the biochemist from Japan, Kikunae Ikeda first isolated it from an edible seaweed Kombu. In 1960s, it was in the toxic category list. There was a myth that it can cause Chinese restaurant syndrome. This included headaches and general feeling of discomfort.

But studies showed that it is safe in limited quantities. Hence its use increased. The US FDA has put it in the GRAS group (generally recognized as safe). European Union has put it as a food additive but to use only in limited amounts in foods. It has the E number of E621.
MSG is a flavor enhancer. It gives foods an umami taste and has a savory aroma. Restaurant foods have it in them. Additionally, canned vegetables, soups, deli meats, chips, snack foods, seasoning blends, frozen foods, instant noodles, and condiments contain it. Its sodium content is one-third of common salt and it increases flavor. Hence people prefer to use it over the regular salt especially to keep blood pressure under control.
MSG symptom complex
There were reports that some people had following cluster of symptoms after consuming MSG. These included headaches, sweating, flushes, face pressure, feeling of tightness over the face, lack of sensations over face, tingling or burning around face, neck and other regions of body, palpitations, chest pain, nausea, weakness, and feeling sick.

But researchers found no clear cut link between MSG intake and these symptoms. Those who had the symptoms had no threat to their lives. The symptoms were mild and patients recovered with no treatment in a short time. Such people can opt to avoid foods that have MSG in them.
Other Controversies
MSG is made by fermenting carbs (sugar beet, sugarcane and such molasses). There were claims that it can increase appetite and cause weight gain and obesity. But multiple studies gave variable results. Hence more large scale studies are essential to confirm this hypothesis. Moreover, people believed that it can cause metabolic diseases. Animal studies showed that it increases risk of diabetes type 2. It elevates insulin resistance and this results in obesity and high blood sugars. However, studies in this direction offered contradictory results.
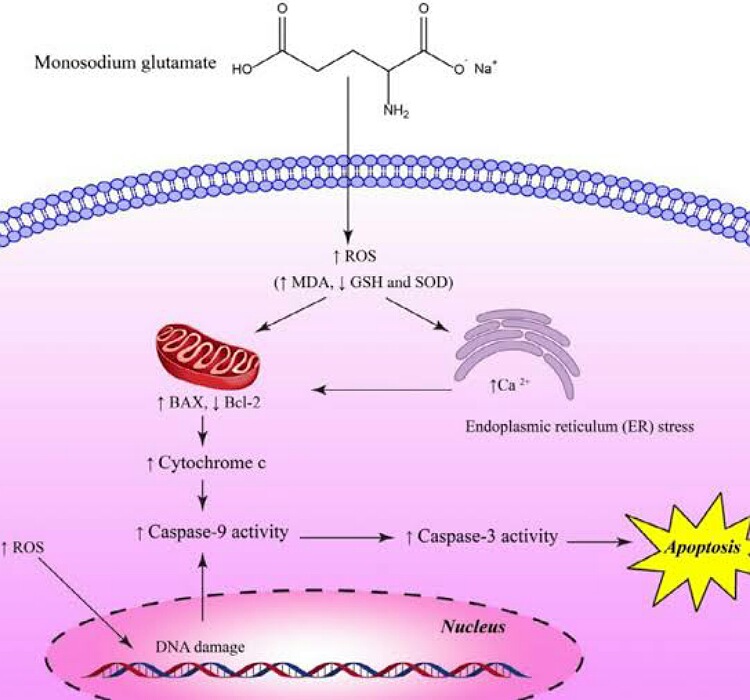
Glutamate is one of the several neurotransmitters in the human body. Certain studies said that MSG would cause a rise of glutamate in the brain. Hence it could lead to brain cells death. But further studies refuted this claim saying that MSG does not get absorbed or cross blood brain barrier.
Also, read 5 Chinese food dishes in Chinese restaurants of the USA that are not authentic!
However, 1% of the population may show symptoms with consumption of 3 or more grams of MSG. A typical serving of foods with MSG has just less than half a gram in it. Hence it is safe to consume such foods. But those who are sensitive to MSG might choose to avoid such foods and canned products.
