Vitamin D is an important vitamin for bone and teeth health. This sunshine vitamin can synthesize in the body with mere sun exposure. But in places where sun is less or during months when sunshine is limited, vitamin D supplements are prescribed. Are these effective? A new US study has shown that these vitamins are a waste of time, money, and efforts.
The sunshine vitamin, vitamin D
Vitamin D or the sunshine vitamin is absolutely essential for the body. It is needed for bone and teeth health. Studies have shown that it can prevent fractures and make bones stronger. Other studies have demonstrated its benefits in easing symptoms in psoriasis, for reducing risk of cardiovascular diseases and also cancer.

Sun exposure can help in synthesis of this vitamin under the skin. But often, people stay more indoors or the sun intensity or duration is not sufficient enough. This can happen in cold winters in temperate regions of the world. This causes vitamin D deficiency. Other genetic and absorption factors also affect its levels in blood.
In the UK, 1 in 6 adults and 1 in 5 children have insufficient vitamin D in their body and blood. Doctors often prescribe vitamin D supplements for prevention and treatment of this vitamin deficiency. But does it help?
The new study on vitamin D supplements
An American study on 25000 people revealed that vitamin D and omega 3 fatty acids in women over age 55 and men overage 50 offer no benefit. Popping those huge pills are a waste of time, money, and efforts, says the study. The study says:
“Supplemental vitamin D3, as compared with placebo, did not have a significant effect on total fractures.”
The study showed that 12927 participants were on this vitamin D supplementation. And 769 of them had fractures. While in the placebo group, 782 people out of 12944 had developed fractures. The difference was insignificant.
Tim Spector, a genetic epidemiologist at King’s College London who has penned several books on nutrition and gut health, tweeted:
“Latest massive VITAL study confirms what I have been saying for a decade – Vitamin D supplementation doesn’t work! It doesn’t reduce fractures even in those with low vit D levels. Let’s sunbathe & eat real food instead and stop measuring vitamin D levels.”
The same study stressed that this vitamin in no way prevents cardiovascular diseases or cancer.
Other conclusions of the study
Dr Sarah Berry is an associate professor of nutritional sciences at King’s College London. She is the chief scientist at personal nutrition company, ZOE, that Tim founded. She explains:
“What these studies tell us is that unless a person is vitamin D deficient, there appears to be no benefit to taking vitamin D in midlife.”
But this supplementation is not totally useless. People with documented deficiency in blood get benefits with it. Sarah adds:
“This doesn’t mean that other groups wouldn’t benefit from supplementation, it just means that supplementation without need is unlikely to help,”
She adds:
“Other studies, including our own ZOE studies, looking at vitamin D supplementation and Covid show that it moderately improved outcomes in some groups.”
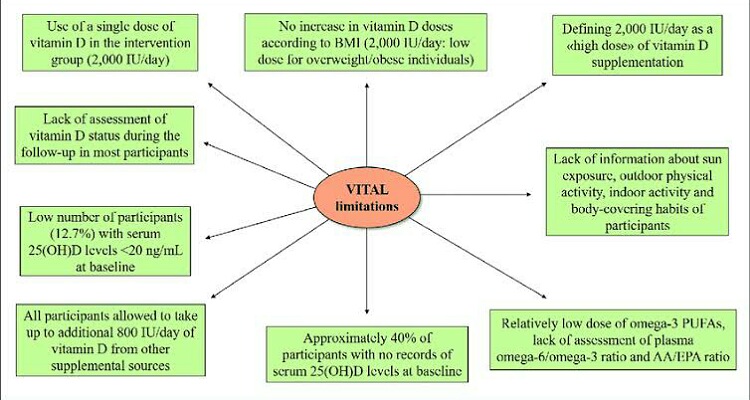
The VITAL study is not without flaws. Firstly very few people in the research group had vitamin D deficiency at the start of the study. And some in the placebo group was also on 20 micrograms of vitamin D daily. Hence the study is not well-controlled.
Therefore, the best approach would be to test blood levels for this vitamin D deficiency and give the supplements only to those who need it. But vitamin D rich diet would be the best and affordable option in the long run for such people. Eggs, fatty fish, and sun-kissed mushrooms have good amounts of vitamin D in them. Some foods are fortified with this vitamin and are therefore healthy.
Read here: Nutritional pills, food supplements, and vitamin consumption increased in Europe in last two years!
Vitamin D supplementation for at risk group
Also, supplementation is good for at risk people. Sarah opines:
“Supplementation is a safe option to help ensure people at risk don’t become deficient. But everyone should know their personal need to supplement. Taking into consideration other health conditions and other factors including sun exposure and dietary intake of vitamin D can help.”