Agriculturists are genetically modifying foods to increase the quantity and nutritional values of these food items.
These are genetically modified foods or genetically engineered foods or bioengineered foods. Are they healthy? Any long-term bad implications of eating them?
Genetically modified foods
Genetically modified foods are those foods whose DNA has been changed to suit our needs. By doing so, agriculturists aim to improve the number of crops.
The plant might either bear more fruits or grains or the sizes of these edible parts might be more. In some crops, the nutritional amounts get increased by these genetic changes.
For instance, the new GM African corn has more folate, vitamin C, and beta-carotene compared to traditional corn. This modification is also sought to increase the resistance of the foods to pests.
Thus the use of pesticides is lessened and humans and the environment are saved from their harmful effects. Megan L. Norris, a biomedical researcher at the UT Southwestern Medical Center states:
“Instead of having to be sprayed with a complex pesticide, these crops come with an innate ‘pesticide’,”

The foods also get cheaper due to more yields. The growth of these plants might be faster. Hence the farmer can have more crops in a year.
Despite the above, many health enthusiasts are concerned that such artificial means might create health troubles for consumers, especially in the long run.
Examples and processes of Genetically modified (GM) foods
We might have eaten such GM foods even without realizing it. The process is of two types. Firstly, it can be done via a slow process of cross-breeding between crops.
But nowadays, more and more scientists are adopting the second shortcut method of modification by editing plant DNA in laboratories. In 2018, more than 92% of corn sold in the USA had a genetic modification.
And 94% of soybean in the USA was from genetically modified seeds of the plant.
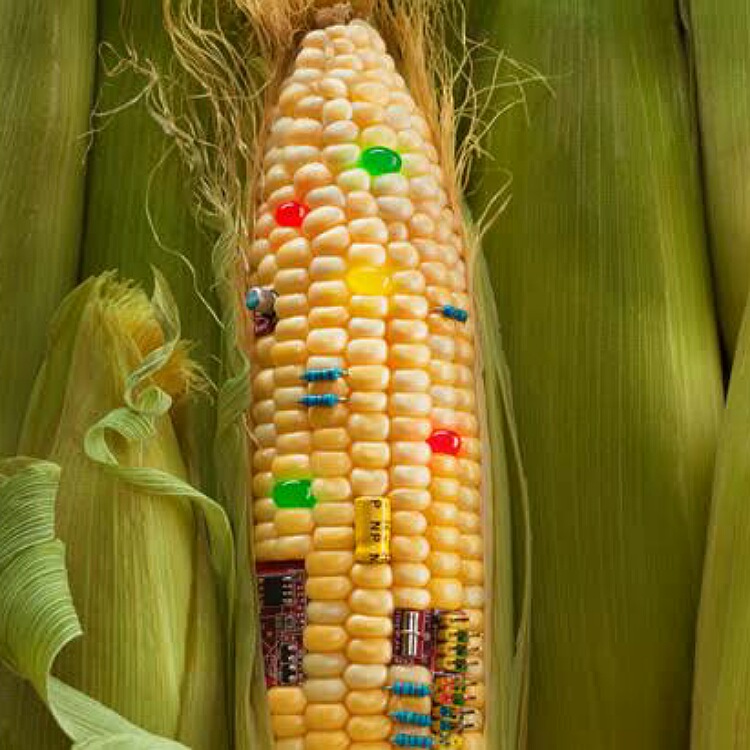

Plant researchers follow the below steps to produce GM crops:
1. They identify the particular genes in a plant that is responsible for a particular trait that they desire in the plant product. These include the size of fruits, the resistance of foods to pests, and the like.
2. The scientists then create copies of these particular genes in the laboratories.
3. They insert these copies into the DNA of the plant cells.
4. These modified cells are used to grow the plants with desired goodness. These are tested and reviewed before widespread use.
Disadvantages of GM foods
GM foods are not without health risks. They can lead to allergic reactions in some sensitive individuals.
The DNA of the organism used in the plant cells might cause allergy and not the original food. Soybean with the DNA of Brazil nuts caused allergies in people with nut allergies.
Also, read Food fusion: popularity, advantages, types, and history!
If there is an antibiotic-resistant gene in the plant cells, it does not get digested and might enter the sewerage system through the feces.
These substances might enter harmful bacteria in the sewers and gut and make them resistant to common antibiotics. This would trigger a bad infectious outbreak.
The rigorous testing in the food regulation labs of countries ensures that GM crops are safe to consume. Megan says:
“I consume GM products and feed them to my family without hesitation.”